ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL ASSISTANCE FROM INTERNATIONAL FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS TO MOLDOVA
DOI: https://doi.org/10.36004/nier.es.2022.1-03
Chief specialist-expert Rossotrudnichestvo
PhD student, Academy of Economic Studies of Moldova
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3831-8132, e-mail: [email protected]
ABSTRACT
The article considers the financial assistance of international financial institutions (the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank) to Moldova in their partnership process. The relevance of the study is determined by the objective need to use this financial assistance to solve urgent financial and economic problems and implement an effective economic policy of Moldova. The purpose of the article is to analyze the financial assistance of International Financial Institutions to Moldova to assess the current state and prospects for developing their financial relations. The information base of the research consists of theoretical and methodological scientific studies of foreign and Moldovan economists devoted to the subject under consideration; information materials of official websites of financial organizations.
It is shown that for the entire period of financial support of Moldova by the International Monetary Fund, almost all special credit mechanisms have been implemented. Since 1993, the World Bank has implemented and is financing 118 different projects (90 completed, 18 active and 7 under development). Agriculture accounts for the largest number of projects financed by the bank. It is revealed that the country's debt and overdue obligations to International Financial Institutions have an upward trend, which is due to the crises and financial instability of 2008 and 2019. The continuation of such a trend in the future may lead to certain financial and economic problems if the financial assistance received does not lead to significant development of the Moldovan economy.
Keywords: International financial institutions, international finance, international financial assistance, emerging markets, economic crisis.
Articolul relevă asistența financiară acordată de Instituțiile financiare internaționale (Fondul Monetar Internațional și Banca Mondială) Moldovei în procesul de cooperare în calitatea lor de parteneri. Relevanța studiului este determinată de necesitatea obiectivă de a utiliza această asistență pentru a rezolva problemele financiare și economice stringente ale țării și a promova o politică economică eficientă. Scopul articolului este de a analiza asistența financiară acordată de instituțiile financiare internaționale Moldovei pentru a evalua starea actuală și perspectivele de dezvoltare a relațiilor cu acestea. Articolul se bazează pe studii științifice teoretice și metodologice ale economiștilor străini și moldoveni, axate pe problematica în cauză, materiale informative ale site-urilor web oficiale ale organizațiilor financiare.
Pe toată perioada sprijinului financiar acordat Moldovei de către Fondul Monetar Internațional au fost implementate aproape toate mecanismele speciale de creditare existente. Din 1993, Banca Mondială a finanțat și continua să finanțeze 118 proiecte diferite (90 au fost finalizate, 18 sunt active și 7 în curs de elaborare). Cel mai mare număr de proiecte finanțate de Bancă revine agriculturii. Datoria și obligațiile restante ale țării față de instituțiile financiare internaționale au o tendință ascendentă, determinată de crizele și instabilitatea financiară din anii 2008 și 2019. Continuarea acestei tendințe în viitor se poate solda cu anumite probleme economice, dacă asistența financiară nu va contribui la o dezvoltare semnificativă a economiei moldovenești.
Cuvinte-cheie: instituții financiare internaționale, finanțe internaționale, asistență financiară internațională, piețe emergente, criză economică.
В статье рассматривается финансовая помощь международных финансовых институтов (Международного валютного фонда и Всемирного банка) Молдове в рамках сотрудничества. Актуальность исследования определяется объективной необходимостью использования оказанной финансовой помощи для решения неотложных финансово-экономических проблем и проведения эффективной экономической политики в Молдове. Цель статьи является анализ финансовой помощи, оказанной международнмих финансовыми институтами Молдове, для оценки современного состояния и перспектив развития их финансовых взаимоотношений. Статья основывается на теоретических и методологических научных исследованиях зарубежных и молдавских экономистов, посвященных рассматриваемой тематике, информационных материалах официальных сайтов финансовых организаций.
Следует отметить, что за время финансовой поддержки Молдовы Международным валютным фондом были использованы практически все специальные кредитные механизмы. Начиная с 1993г. Всемирный банк финансировл 118 различных проектов (90 были завершенны, 18 находятся на стадии реализации и 7 - на стадии разработки). Наибольшее количество профинансированных Банком проектов приходится на сельское хозяйство. Выявлено, что задолженность и просроченные обязательства страны перед международными финансовыми институтами имеют отчетливую тенденцию к повышению, которая обусловлена кризисами и финансовой нестабильностью 2008 и 2019 гг. Сохранение такой тенденции в будущем может привести к определенным финансово-экономическим проблемам, если полученная финансовая помощь не будет способствовать значительному росту экономики Молдовы.
Ключевые слова: Международные финансовые институты, международные финансы, международная финансовая помощь, развивающиеся рынки, экономический кризис.
![]()
JEL Classification: E69, F21, F33, F35.
UDC: 339.726+339.732+339.727.3
INTRODUCTION
In modern conditions of the global economic world order, the International Financial Institutions (IFI) play an important role. They are now a key element of the international financial system. Significant amounts of financial resources, scientific and economic potential and international prestige allow IFIs to have a significant impact on the economic development of many countries and regions of the world. The article deals with the main world IFIs: the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank Group (WB).
Moldova, like other emerging market economies, is in the process of integrating into the international financial system. Its membership in the structures of IFIs makes it possible to use the financial resources to intensify this process. The global economic crisis of 2008 and the economic consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic have caused serious challenges, both for the entire system of the global world economy and its financial component. During the period of crisis, countries with developing market economies find themselves in a very difficult financial and economic situation. In this regard, to solve the urgent financial and economic problems that have arisen and to conduct an effective financial and economic policy for the development of its economic system, the Moldova objectively needs financial assistance from IFIs.
LITERATURE REVIEW
Foreign and Moldavian economists devoted their scientific works to the problems related to some aspects of the subject under consideration in this article. In the article (Kregel, 2018), special attention is paid to offsetting the lack of domestic savings with external financing in the form of soft loans as part of official assistance from international financial institutions. It is shown that the financing of economic development should be carried out through the comprehensive use of national financial institutions and the stimulation of employment in domestic manufacturing and export-oriented industries. The essence of foreign direct investment was analyzed by Dunning (1988) and Markusen (2000). Various aspects of financial assistance to developing countries in order to promote their economic and social development, as well as to expand the mechanism for their concessional lending to the World Bank, are considered by the US Congress in a study (Congress U.S., 2020). The role of the World Bank in promoting participatory budgeting (PB) with partners is discussed by Goldfrank (2012). WB is shown to have little effect on PB outcomes in different countries since there is no way to control many influencing factors. Nevertheless, there is great practical potential in the implementation of PB procedures. Vilpišauskas (2019) studied the strategies and approaches of the main International Financial Institutions — the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank to reforms in the Eastern Partnership countries (Belarus, Moldova and Ukraine). It is noted that in addition to the traditional recommendations for fiscal consolidation and structural reforms, IFIs in these countries are focusing on reforms in the most corrupt sectors — banking and energy. The article by Lopotenco (2020) focuses on the vulnerability of the economy of Moldova and especially its financial system to the economic crisis caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. It is revealed that this vulnerability is mainly related to the specifics of the country's economy (small, open economy, with a constant current account deficit and a strong dependence on international financial flows). The study conducted by Stratan (2020) analyzes the role and approach of the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank in developing and supporting Moldova to overcome the COVID-19 crisis. It is shown that these organizations have made an urgent contribution to provide emergency financial assistance to mitigate the economic consequences of COVID-19, especially to stabilize the country's balance of payments. The role of international financial flows in stimulating the economic growth of Moldova was analyzed by Железнова, Хынку (2011).
RESEARCH METHODS
As a practical basis, the article uses the scientific works of Moldovan and foreign scientists on international financial flows and investments. The methodological basis of the study includes: causal relationships of the phenomenon under study, mechanisms and financial flows of Moldova within the framework of financial assistance provided by the IMF and the WB; statistical methods of data analysis (quantitative, qualitative, comparative). The charts presented in this article are implemented in Excel. The source of factual data on IFI financial assistance to Moldova is the official websites of the IMF and WB. The source of the country's financial and economic data is the official website of the National Bank of Moldova.
RESEARCH RESULTS
Currently, Moldova has the following agreements with the IMF on special lending facilities (National Bank of Moldova, 2021):
mechanism of compensatory and reserve financing (Compensatory and Contingency Financing Facility, CCFF);
a systemic transformation mechanism for financing structural transformations (Systemic Transformation Facility, STF);
Stand-by agreement (SBA) — for certain purposes agreed with the IMF;
an extended financing mechanism (Extended Fund Facility, EFF) — to provide funds for long periods and in larger amounts in relation to quotas than is provided for in the country's usual credit shares. The basis for granting a loan is a serious violation of the balance of payments;
an extended credit facility (Extended Credit Facility, ECF) provided on concessional terms in order to reduce poverty and promote economic growth;
concessional lending under the Rapid Financing Instrument (RFI) and the Rapid Credit Facility (RCF).
In connection with the socio-economic crisis associated with the COVID-19 pandemic, for low-income countries, including Moldova, in 2020, the IMF opened access to concessional lending under the Rapid Financing Instrument (RFI) and the Rapid Credit Facility (RCF) (IMF, 2021a).
It should be noted that the ECF and EFF lending mechanisms are used to eliminate a serious imbalance in the balance of payments, as well as to reduce poverty and promote economic growth. At the same time, these credit facilities have been used by the IMF regularly for lending to Moldova since 1996. The last lending under these facilities was made on 20.12.2021 (IMF, 2021a). That is, from 1996 to the present, the problem of balance of payments violations and poverty reduction in Moldova has not been finally resolved. During the entire period of financial support to Moldova, starting from 1993, the IMF has been involved in almost all special credit mechanisms. Also, the IMF has carried out annual consulting in the country in the field of financial and economic policy, including the central bank's policy.
Let's consider the dynamics of Moldova's debt on the IMF loan since 1993. Figure 1 shows the graph of changes in the debt on the IMF loan of Moldova in SDR from 1993 to 2021 (IMF, 2021b).
Figure 1.
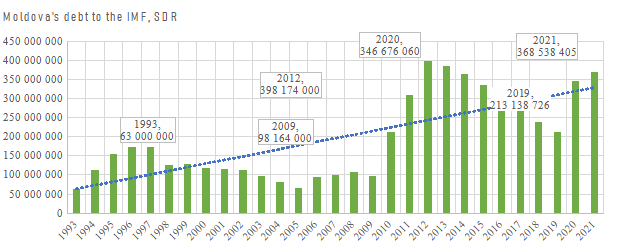
Change in the total debt of Moldova under the IMF loan
Source: developed by the author according to the IMF
The data in Figure 1 show that the total debt of Moldova since 1993 on various IMF loans has an upward trend (63 million SDR in 1993, 346.676 million SDR and 368.538 million SDR in 2020 and 2021, respectively). The consequences of the global economic crisis of 2008 affected the financial and economic situation of the country — the debt to the IMF increased sharply: from 98,164 million SDR in 2009 to 398,174 million SDR in 2012 (the maximum for the entire time of partnership with the IMF). The economic and social consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic have led to a significant increase in Moldova's debt to the IMF compared to pre-crisis 2019. As of 31.12.2021, the country's debt on IMF loans reached SDR 368.538 million (about 516 million US dollars) (IMF, 2021b), which is less than its maximum value in 2012, but over 3.7 times more than in 2009. Thus, the data in Figure 1 demonstrate that during the periods of crisis and financial instability in 2008 and 2019, to solve the urgent financial and economic problems of Moldova and implement a policy to stabilize its economic system, the IMF has dramatically increased its financial assistance to the country. The growth of this financial assistance was reflected by a significant increase in the total debt of Moldova to the IMF after 2008 and 2019 and the preservation of its overall upward trend.
At the same time, the volumes of overdue obligations and projected payments of the country to the IMF as of 02/28/2022 also have an upward trend (Figure 2) (IMF, 2021c). The maximum volume of payments is projected for 2024 — 79.11 million SDR.
Figure 2.
Change in the volume of overdue obligations and projected payments of the country to the IMF
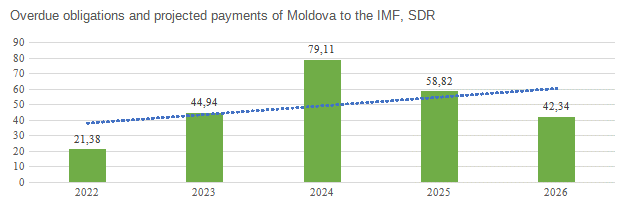
Source: developed by the author according to the IMF
Such a significant amount of payments on overdue obligations means that the country may face certain economic and financial problems in the future. Moreover, if borrowing from the IMF does not lead to significant development of Moldova's economy, these problems will grow every year. Therefore, the financial resources received by the country from the IFI should be used for its economy with maximum efficiency.
Significant support to Moldova is provided by the World Bank Group, which from 11.03.1993 to 05.11.2021 took and is taking part in financing 118 different projects (The World Bank Group, 2021a). The total amount of funding for these projects amounted to 2,013.66 million US dollars, including:
90 completed projects — 1,192. 26 million US dollars;
18 active projects — 636.58 million US dollars;
7 projects under development — 184.82 million US dollars.
3 cancelled projects.
Accordingly, the World Bank has allocated 821.4 million US dollars for 7 projects under development and 18 active projects (25 projects in total) implemented over the past 9 years. Moreover, totally 1,192.26 million US dollars were spent on all 90 completed projects over 19 years. That is, over the past 9 years, the intensity of the World Bank's project financial assistance to the country has sharply increased.
Figure 3 shows data on the obligations of Moldova to the World Bank Group from 2014 to October 2021 (in millions of US dollars) (The World Bank Group, 2021b).
Figure 3.
Obligations of Moldova for financial years to the World Bank Group
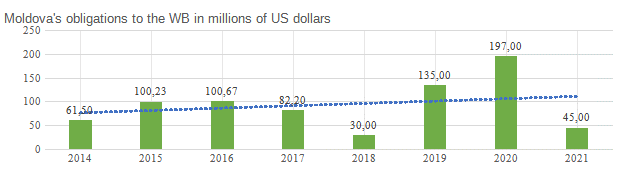
Source: developed by the author based on data from The World Bank Group
The diagram in Figure 3 shows that the lending of projects in Moldova by the World Bank Group has increased significantly since the beginning of the COVID-19 crisis compared to previous years. Currently, the bulk of the WB's financial resources is directed to the implementation of urgent medical projects and projects related to the elimination of the consequences of the socio-economic crisis from the COVID-19 pandemic. This makes it possible for the Government not to divert significant financial resources from other important socio-economic programs.
The number of projects by category of economic topics financed by the World Bank Group in Moldova from 11.03.1993 to 23.04.2021 are presented in Table 1 (The World Bank Group, 2021c).
Table 1
Number of projects in Moldova by category of economic topics funded by the World Bank Group
World Bank projects on themes of economics |
Number of projects |
Rural services and infrastructure |
18 |
State-owned enterprise restructuring and privatization |
9 |
Public expenditure, financial management and procurement |
9 |
Micro, Small and Medium Enterprise support |
9 |
Rural markets |
10 |
Administrative and civil service reform |
10 |
Rural policies and institutions |
11 |
Education for all |
11 |
Regulation and competition policy |
15 |
Climate change |
16 |
TOTAL |
118 |
Source: developed by the author based on data from The World Bank Group
The data in Table 1 show that the largest number (39) of World Bank-funded projects falls on agriculture, a key sector of the Moldovan economy. In second and third place are projects related to climate change (16) and regulation of competition policy (15). The number of other projects financed on economic topics is approximately equal.
CONCLUSIONS
A study of the financial assistance provided by the IFI to Moldova showed that the country's financial cooperation with the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank Group is carried out in all financial and economic aspects that are in the assets of these organizations. It has been established that all the main special credit mechanisms used by the IMF are involved in this process, and the World Bank Group has participated and is participating in lending 118 projects on various topics since 1993. The largest number of credited projects (39) falls on agriculture, a key sector of the Moldovan economy. At the same time, over the past 9 years, the intensity of the World Bank's project financial assistance to the country has increased dramatically. It was revealed that the IMF's financial assistance is regularly provided to reduce poverty and promote economic growth, as well as to eliminate the country's balance of payments deficit caused by unfavorable changes in the structure of its economy. That is, since the beginning of financial cooperation between Moldova and the IMF, this situation has not changed for the better. The data on the dynamics of the total volume of debt to IFIs, overdue obligations and projected payments of Moldova to the IMF allow us to conclude that their upward trend is due to the periods of crisis phenomena and financial instability in 2008 and 2019. The continuation of this trend in the future may lead to certain economic and financial problems if borrowing from IFIs does not lead to significant development of the Moldovan economy.
In this regard, it would be economically feasible for the IMF and the WB to allocate financial resources on a permanent basis to improve the financial and economic stability of Moldova, in particular, to eliminate the problem areas of key sectors of its economy (these include the agricultural and banking sectors). Improving the structure of the key sectors of the Moldovan economy will have an impact on the entire economic system of the country as a whole and its economic stability. Thus, the results of financial cooperation with IFIs and their role in the economic development of Moldova could be much more significant if the specifics of its economic system are taken into account, and the efficiency of using the financial resources of these organizations is increased.
REFERENCES
Congress, U. S. (2020). Multilateral Development Banks: Overview and Issues for Congress. Congressional Research Service. https://crsreports.congress.gov/product/pdf/R/R41170
Dunning, J. H. (1988). Explaining International Production. London: Unwin Hyman.
Goldfrank, B. (2012). The World Bank and the Globalization of Participatory Budgeting, Journal of Public Deliberation, 8, 2. https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/0ee3/41760f6ac48055efe2daf5d56f8898f82e74.pdf?_ga=2.55679979.1975371505.1650129349-665675.1646414585
IMF. (2021a). Moldova and the IMF. https://www.imf.md/imfmold.html
IMF. (2021b). Moldova, Republic of: Credit Outstanding as of November 30 2021. https://www.imf.org/external/np/fin/tad/exportal.aspx?memberKey1=672&category=EXC
IMF. (2021c). Moldova, Republic of: Financial Position in the Fund as of November 30, 2021. https://www.imf.org/external/np/fin/tad/exfin2.aspx?memberKey1=672&date1key=2099-12-31
Lopotenco, V. (2020). The Financial System Challenges of the Republic of Moldova in the Pandemic COVID 19 Context. International Journal of Innovative Technologies in Economy, 4(31), 1-5. https://doi.org/10.31435/rsglobal_ijite/30092020/7170
Markusen, J. R. (2000). Foreign Direct Investment and Trade. Adelaide: University of Adelaide.
National Bank of Moldova. (2021). Relations with the International Monetary Fund (IMF). https://www.bnm.md/en/content/relations-international-monetary-fund-imf
Stratan, I. (2020). The role of the development partners in the Republic of Moldova in the context of the COVID-19. Univers strategic, 3(43), 79-89.
The World Bank Group (2021a). Projects. https://projects.worldbank.org/en/projects-operations/projects-list?lang=en&&=&countrycode_exact=MD&os=0
The World Bank Group (2021b). The World Bank in Moldova. https://www.worldbank.org/en/country/moldova/overview
The World Bank Group (2021c). Projects. http://projects.worldbank.org/search?lang=en&&&searchTerm=&countrycode_exact=MD
Vilpišauskas, R. (2019). Strategies and Approaches of International Financial Institutions towards Eastern Partnership Countries. EU-STRAT Working Paper, 14, 3-38. http://eu-strat.eu/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/EU-STRAT-Working-Paper-No.-14.pdf
Железнова, Н., Хынку Р., & Железнова, Е. (2011). Основы функционирования рынка капитала. Кишинев: МЭА.
Крегель, Я. (2018). Теория Мински: международное финансирование развивающихся стран. Экономическая политика, 13, 4, 8-19. https://doi.org/10.18288/1994-5124-2018-4-01