THE IMPACT OF ENVIRONMENTAL REGULATIONS ON FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT: A LITERATURE REVIEW
IMPACTUL REGLEMENTĂRILOR DE MEDIU ASUPRA INVESTIȚIILOR STRĂINE DIRECTE: O REVIZUIRE A LITERATURII DE SPECIALITATE
ВЛИЯНИЕ ЭКОЛОГИЧЕСКОГО ЗАКОНОДАТЕЛЬСТВА НА ПРЯМЫЕ ИНОСТРАННЫЕ ИНВЕСТИЦИИ: АНАЛИЗ ЛИТЕРАТУРЫ
;DOI: https://doi.org/10.36004/nier.es.2022.2-09
UDC: 339.727.2+349.6
JEL classification: Q56, F21, M40, Q01.
Anatol Melega
PhD student
Academy
of Economic Studies of Moldova
Stefan cel Mare University of
Suceava
ORCID: 0000-0003-4763-0520
Abstract
Foreign direct investment (FDI) is essential for the global economy, especially for developing and emerging countries, which are dependent on these financial resources. Governments compete to attract foreign investors by offering tax incentives, strong regulatory frameworks and flexible environmental regulations. While some countries relax environmental regulations to attract FDI, others implement stricter measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and protect the environment. The aim of this article is to present a thorough and up-to-date review of the literature that has focused on the analysis of the correlation between FDI and environmental regulations. The bibliometric analysis focuses on the main concepts that elucidate the relationship between environmental regulations and SDI, highlighting current trends and theories. This research is crucial for understanding the influence of environmental regulation on FDI and its effects on economic development and environmental conservation worldwide. According to the literature, the pollution haven theory has received substantial support, indicating that nations with permissive regulations attract more foreign direct investment due to lower business costs. The literature indicates strong support for the pollution haven theory, suggesting that countries with relaxed regulations attract more FDI due to lower business costs. The results of this study could help inform the development of environmental policies and strategies to attract foreign investment and address climate change and environmental degradation. At the same time, this research provides valuable information for researchers as it highlights the main research niches that need to be addressed and analysed.
Keywords: foreign direct investment, determinants, environmental regulations, pollution haven theory, race to the top theory
Investițiile străine directe (ISD) sunt esențiale pentru economia globală, în special pentru țările în curs de dezvoltare sau emergente, care sunt dependente de aceste resurse financiare. Guvernele concurează pentru a atrage investitorii străini prin oferirea de stimulente fiscale, cadre de reglementare puternice și reglementări flexibile în materie de mediu. În timp ce unele țări relaxează reglementările de mediu pentru a atrage ISD, altele implementează măsuri mai stricte pentru a reduce emisiile de gaze cu efect de seră și pentru a proteja mediul. Scopul acestui articol este de a prezenta o analiză amănunțită și actualizată a literaturii de specialitate care a avut drept topic analiza corelației dintre ISD și reglementările privind protecția mediului. Analiza bibliometrică se concentrează asupra principalelor concepte care elucidează relația dintre reglementările de mediu și ISD, evidențiind tendințele și teoriile actuale. Această cercetare este crucială pentru înțelegerea influenței reglementărilor de mediu asupra ISD și a efectelor acesteia asupra dezvoltării economice și conservării mediului la nivel mondial. Conform literaturii de specialitate, teoria paradisului de poluare a primit un sprijin substanțial, indicând faptul că națiunile cu reglementări permisive atrag mai multe investiții străine directe datorită costurilor reduse ale afacerilor. Literatura de specialitate indică un sprijin puternic pentru teoria paradisului de poluare, care sugerează că țările cu reglementări relaxate atrag mai multe investiții străine directe datorită costurilor mai mici pentru întreprinderi. Rezultatele acestui studiu ar putea ajuta la elaborarea de politici și strategii de mediu pentru a atrage investiții străine și pentru a aborda schimbările climatice și degradarea mediului. Totodată această cercetare oferă informații valoroase pentru cercetători, datorită faptului că evidențiază principalel nișe de cercetare care necesită a fi abordate și analizate .
Cuvinte-cheie: investiții străine directe, factori determinanți, reglementări de mediu, teoria paradisului poluării, teoria cursei în sus
Прямые иностранные инвестиции (ПИИ) играют важную роль в мировой экономике, особенно для развивающихся стран и стран с развивающимися рынками, которые зависят от таких финансовых ресурсов. Правительства конкурируют за привлечение иностранных инвесторов, предлагая налоговые льготы, сильную нормативную базу и гибкие экологические нормы. В то время как некоторые страны смягчают экологические нормы для привлечения ПИИ, другие принимают более строгие меры для сокращения выбросов парниковых газов и защиты окружающей среды. Цель данного исследования - представить подробный и актуальный обзор литературы, посвященный анализу взаимосвязи между ПИИ и экологическим регулированием. Библиометрический анализ фокусируется на основных концепциях, проясняющих взаимосвязь между экологическим регулированием и ПИИ, выделяя современные тенденции и теории. Данное исследование крайне важно для понимания влияния экологического регулирования на ПИИ и его последствий для экономического развития и сохранения окружающей среды во всем мире. Согласно литературе, теория "убежища от загрязнения" получила значительную поддержку, указывая на то, что страны с разрешительным регулированием привлекают больше прямых иностранных инвестиций из-за более низких затрат на ведение бизнеса. В литературе отмечается значительная поддержка теории "убежища от загрязнения", согласно которой страны со смягченным регулированием привлекают больше ПИИ из-за более низких затрат на ведение бизнеса. Результаты данного исследования могут помочь в разработке экологической политики и стратегий для привлечения иностранных инвестиций и решения проблем изменения климата и деградации окружающей среды. В то же время, данное исследование предоставляет ценную информацию для исследователей, поскольку оно выделяет основные исследовательские ниши, которые необходимо рассмотреть и проанализировать.
Ключевые слова: прямые иностранные инвестиции, детерминанты, экологические нормы, теория оазиса загрязнения, теория гонки за вершиной
In light of the present scenario where environmental concerns and climate change are growing more urgent, comprehending the interconnection between environmental policy and the attraction of foreign direct investment is imperative. According to the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), "environmental regulations are policies and legal instruments established by governments to protect the environment, human health and natural resources; these regulations aim to prevent or minimise pollution, waste and other harmful effects on the environment caused by human activities." Environmental regulations hold a crucial position in ensuring the sustainable growth of a country's economy, as well as in creating a favorable business environment. Consequently, national governments are encouraging investment in significant ventures of polluting industries, with the objective of curtailing carbon emissions. A growing number of studies highlight the relationship between these issues (Wang & Li, 2021), forming a growing debate on the effectiveness and consequences of different approaches to environmental regulation and attracting foreign direct investment (ISD).
Certain nations have implemented rigorous regulations to combat greenhouse gas emissions and safeguard the environment. Conversely, some have adopted a flexible stance to allure foreign direct investment. Bearing this in mind, the scholars probed several hypotheses that aimed to elucidate the correlation between the level of environmental regulations in effect and the magnitude of international direct investment in those nations. In short, the debate on environmental regulation and ISD attraction has broadened and now encompasses several theories. In the following we present the most popular theories in the literature:
Polllution Haven Theory: This theory argues that companies tend to shift their production and investment to countries with more relaxed environmental regulations in order to reduce costs and avoid the restrictions imposed by stringent regulations (Nasir, Huynh & Tram, 2019). This theory stresses the need to address the problem through an international framework, thereby ensuring that tax havens do not undermine global environmental protection efforts.
True Cost Theory: states that strict environmental regulations will lead to more sustainable and efficient production in the long run. Businesses that comply with these regulations will be able to reduce their long-term costs and protect their reputation with stakeholders (Caetano, Marques, Afonso & Vieira, 2022). Therefore, this theory stresses the importance of transparency and communication within companies to implement and monitor the effects of these regulations.
According to the Convergence Theory, countries that experience economic growth will eventually encounter increasing pressure from various stakeholders to implement more rigorous environmental regulations. This would ultimately lead to all nations adopting comparable environmental regulations, as observed by Nguyen (2022). Therefore, promoting favorable regulatory convergence requires nations to work together, sharing their best practices and collaborating on environmental policies.
Race to the top Theory: believes that countries that introduce increasingly stringent environmental regulations will create a competitive advantage due to sustainable and durable products and services, which will attract ISD and contribute to sustainable development (Du, Cheng & Yao, 2021). Given this theory, promoting proactive policies to boost innovation and competitiveness is particularly important.
Transaction Costs Theory: suggests that strict regulations will contribute to higher transaction costs for companies investing in foreign countries. This is because the implementation of strict regulations requires additional resources to comply, thus investments become costly and risky (Duzbaievna Sharapiyeva, Antoni & Yessenzhigitova, 2019). This theory highlights the need to balance transaction costs with the benefits of strict environmental regulations, while promoting collaboration between the public and private sectors to develop innovative and efficient solutions to manage these costs.
These theories offer varying viewpoints regarding the correlation between environmental regulations and foreign direct investment (ISD). Notably, the pollution haven theory and the race to the top theory present conflicting arguments on how regulations impact ISD attraction. As a result, the literature in this area is extensive and controversial. Although there are numerous studies addressing different aspects of this topic, only a few have applied a bibliometric approach. Rezza (2015) analyzed a set of empirical studies exploring the pollution haven theory, providing explanations for the differences in their results.
This paper aims to make new contributions through a comparative analysis of existing theories and relevant studies. By carefully reviewing the literature and applying rigorous bibliometric methods, the paper identifies current trends and possible future research directions in the field. In addition, the results will provide a solid basis for developing recommendations on environmental policy and strategies to attract foreign direct investment.
Determinants of ISD
Currently, there is an extensive literature on ISD in a country that presents diverse and multifactor approaches to this activity (Osei & Kim, 2020). These involve both macro- and micro-level environmental characteristics (Dinh, Vo, The Vo & Nguyen 2019). Even though there is no general agreement on the main determinants for ISD, authors mention certain determinants very often. The most common one is infrastructure. This determinant considers that good infrastructure facilitates communication, transportation and access to natural resources, which can make a country attractive for ISD (Majeed, Jiang, Mahmood, Khan & Olah, 2021). Another determinant, this time at the micro level, often mentioned in the literature, is the cost of production. Thus, low production costs, such as cheap labour or access to raw materials, can contribute to a country's attractiveness for ISD (Saidi, Mani, Mefteh, Shahbaz & Akhtar, 2020). Another accepted determinant in the literature is the cost of production (Khan, Chenggang, Hussain & Kui, 2021). This determinant can be explained by the fact that low production costs, such as raw materials and cheap labor, make a country more attractive for ISD. The next determinant looks at economic and political stability. Countries that enjoy good economic and political stability significantly reduce investment risks, thus making the country in question more attractive for ISD (Agyapong & Bedjabeng, 2020). The next important factor is tax regulation. Thus, business-friendly tax regulations can make a country more attractive for ISD (Jushi, Hysa, Cela, Panait & Voica, 2021).
Yet, a significant area of research focuses on the effects of various geographic settings and geographies on the connection between environmental regulation and foreign direct investment. The degree to which environmental rules effect foreign direct investment may vary by region according to regulatory frameworks, cultural and social considerations, and economic conditions. The relationship between environmental regulation and foreign direct investment may also be influenced by cultural and social issues, such as views toward the environment. The link between these variables may also be impacted by changes in economic conditions, such as fluctuations in the availability of natural resources or the existence of rival industries. To guide investment strategies and inform policy decisions, a deeper understanding of how regional variations affect the link between environmental regulation and foreign direct investment is required.
Several studies have looked into how cultural and socioeconomic factors affect how environmental regulations and foreign direct investment are related. It has been suggested that social and cultural aspects may have an impact on how foreign investment is impacted by environmental legislation. Companies from cultures where environmental protection is valued more than economic growth, for instance, might favor investing in areas with strict environmental regulations, whereas those from cultures where economic growth is valued more highly might favor investing in areas with laxer regulations. For example, Park and Luo (2001) argue that guanxi, or personal connections and networks, play a significant role in organizational dynamics in Chinese firms. This suggests that companies from different cultural contexts may approach FDI differently depending on their networks and relationships.
Furthermore, public opinion and political views toward environmental regulation can be influenced by cultural and socioeconomic variables, which can therefore have an impact on the regulatory environment for foreign investment. Strong environmental movements may increase the likelihood that nations implement stringent environmental laws, which may either encourage or discourage foreign direct investment. For exemple, Slangen and Van Tulder (2009) suggest that cultural distance, political risk, and governance quality all contribute to external uncertainty variables that can affect FDI decisions. Furthermore, Gereffi, Humphrey, and Sturgeon (2005) highlight the governance of global value chains as a key factor in understanding FDI decisions and outcomes. Cultural and social factors may play a role in shaping the governance structures and power dynamics within these value chains. Giuliani and Meliciani (2021) investigated the impact of cultural and linguistic distances on the relationship between environmental regulation and foreign direct investment in the international location of US firms. Their study found that cultural and linguistic differences can moderate the relationship between environmental regulation and foreign direct investment, suggesting that cultural and social factors should also be considered when examining the impact of environmental regulations on foreign investment. Finally, Chen and Miller (2010) propose an ambicultural approach to management that integrates Western and Eastern perspectives. This could be relevant to FDI decisions and outcomes in cross-cultural contexts, where cultural and social factors may influence the way that environmental regulation is perceived and navigated.
Moreover, it is crucial to remember that other aspects of the relationship between environmental regulation and foreign direct investment, such as the accessibility of natural resources, technical advancements, and economic conditions, can also have an impact. While examining this link, it is important to take into account these elements since they have the potential to either lessen or worsen the effects of environmental regulation on foreign investment.
In general, understanding how cultural, socioeconomic, and other elements may affect environmental regulation and foreign direct investment is essential for policymakers and investors.
Next, we conducted a meta-analysis in Table 1 of the most important studies in the literature that consider the determinants of ISD:
Table 1:
Meta-analysis of the most relevant papers on ISD factors
Authors and year |
Study name |
Results |
General remarks |
Hossain, M. S., Kamal, M. S., Halim, M. R., & Zayed, N. M. (2019). |
„Inward Foreign Direct Investment and Welfare Nexus: the Impact of Foreign Direct Investment on Welfare in Developing Countries.” |
„The influx of foreign direct investment in developing nations can be influenced by factors such as political stability, governance, and socio-economic well-being.” |
„The attraction of foreign direct investment is contingent on crucial factors such as political stability and socio-economic well-being.” |
Yang X, & Shafiq, M.N. (2020). |
„The impact of foreign direct investment, capital formation, inflation, money supply and trade openness on economic growth of Asian countries.” |
„The implementation of advantageous tax policies can incentivize the inflow of foreign direct investment.” |
„The attraction of foreign direct investment can hinge on the implementation of favorable tax regulations.” |
Li, K., Zu, J., Musah, M., Mensah, I. A., Kong, Y., Owusu-Akomeah, M., ... & Agyemang, J. K. (2022) |
„The link between urbanization, energy consumption, foreign direct investments and CO2 emanations: An empirical evidence from the emerging seven (E7) countries.” |
„Foreign direct investment can be impacted by factors such as energy consumption and urbanization.” |
„Factors like energy consumption and urbanization can play a significant role in attracting foreign direct investment.” |
Huynh, C. M. (2021) |
„Foreign direct investment and income inequality: Does institutional quality matter?.” |
„The standard of education can be a determining factor in attracting foreign direct investment.” |
„The standard of education can play a significant role in the attraction of foreign direct investment.” |
Xiao, D., Gao, L., Xu, L., Wang, Z., & Wei, W. (2023). |
„Revisiting the Green Growth Effect of Foreign Direct Investment from the Perspective of Environmental Regulation: Evidence from China.” |
„The adoption and development of green technology can play a significant role in attracting foreign direct investment.” |
„The adoption and development of green technology can play a significant role in attracting foreign direct investment.” |
Balsalobre-Lorente, D., Driha, O. M., Shahbaz, M., & Sinha, A. (2020). |
„The effects of tourism and globalization over environmental degradation in developed countries.” |
„Tourism can be a factor in attracting foreign direct investment.” |
„Tourism is a factor that can significantly impact the attraction of foreign direct investment.” |
Contractor, F. J., Dangol, R., Nuruzzaman, N., & Raghunath, S. (2020). |
„How do country regulations and business environment impact foreign direct investment (ISD) inflows?.” |
„The standard of regulations in a country can impact the attraction of foreign direct investment in developing nations.” |
„Attracting foreign direct investment to developing countries can be influenced by the quality of regulations in place.” |
Li, S., & Fabuš, M.(2019) |
„Study on the spatial distribution of China's Outward Foreign Direct Investment in EU and its influencing factors.” |
„Transport infrastructure can be a crucial factor in attracting foreign direct investment.” |
„The availability of transport infrastructure can play a crucial role in attracting foreign direct investment.” |
Ahmad, M., Jiang, P., Majeed, A., & Raza, M. Y. |
„Does financial development and foreign direct investment improve environmental quality? Evidence from belt and road countries.” |
„Foreign direct investment can be attracted by good infrastructure and financial development.” |
„Infrastructure and finance have a significant impact on attracting foreign direct investment.” |
Source: developed by the author
Based on the meta-analysis presented in the table, we can deduce that numerous factors may have an impact on foreign direct investment. The most significant of these factors are political stability and socio-economic welfare, favorable tax regulations, energy consumption and urbanization, quality of education, green technology, and tourism. Taking these aspects into account, the following hypothesis can be formulated:
H1 Favourable tax regulations, green technology and quality of education are key factors in attracting ISD.
ISD and environmental regulation: theoretical approaches
It is accepted in the literature that foreign direct investment flows are a particularly important factor for economic development, job creation and technology transfer. However, ISD flows are also associated with negative environmental impacts such as pollution, deforestation and carbon emissions. This is why various environmental regulations have been implemented to reduce these negative aspects. Taking these issues into account, there are various theoretical approaches to the relationship between ISD flows and environmental regulations.
One of the important theories is the pollution paradise theory. It suggests that more permissive environmental regulations could attract foreign investment, especially in polluting industries. However, some studies contradict this theory, indicating that a more sustainable and responsible approach to the environment can provide a stable and predictable business environment and a positive reputation, which is beneficial in attracting investor interest1 .
Another theoretical approach is the true cost approach. This offers a similar argument, arguing that strict environmental regulations can bring long-term benefits by promoting sustainable and efficient production and generating a competitive advantage. Recent studies cited in the literature review support this view, demonstrating that strict regulations can improve the financial performance of companies and stimulate innovation. Zeng et al. (2020) found that strict carbon regulations can lead to beneficial innovation outcomes.
On the other hand, the Convergence theory analyzes the relationship between environmental regulation and economic growth, positing that developed countries are more capable of addressing environmental concerns. Nevertheless, Bergh and Löfgren (2014) investigated the connection between economic development and the environment and discovered that „while developed countries may be more proficient in managing environmental issues, they did not observe a distinct convergence in the extent of environmental regulation.” The race to the top theory argues that countries that introduce increasingly stringent environmental regulations will create a competitive advantage over time. In the literature we find a study by Lee and Rho (2020) that studied the impact of carbon regulations on the financial performance of companies and showed that these regulations can indeed attract ISD. Likewise, another study by Delgado-Gómez and Gallego-Álvarez (2020) showed that strict environmental regulations can be a competitive advantage for companies and can lead to sustainable development in the long run.
The last theory examined in this paper is transaction costs and considers that strict regulations will contribute to higher transaction costs for companies investing in foreign countries. In the literature we found only one study that shows that strict regulations increase transaction costs and reduce ISD (Peng & Wang, 2006).
Based on these findings, it can be concluded that the relationship between environmental regulation and ISD is complex and multidimensional. Despite discrepancies between theories, it is clear that a sustainable and responsible approach to the environment can bring benefits to both businesses and national economies. It is therefore important that governments and business work together to develop and implement coherent and effective environmental policies that promote sustainable development and attract ISD in a responsible and equitable way. There are several theories that explore the correlation between environmental regulation and ISD, each providing unique perspectives on how environmental regulations can impact business behavior and national economies. However, the reviewed papers indicate that a large proportion of researchers have focused more on the race to the top theory at the expense of other theories, which is why we formulate H2 of this paper, viz:
H2: The race up theory has the most support in the literature.
This hypothesis can also be tested by comparing the frequency of occurrence of different theories in the literature, thus identifying the theory that is most often addressed and has the greatest impact in the context of ISD and environmental regulation, which we will do in the practical part of this paper.
1 The global apparel value chain, trade and the crisis: Challenges and opportunities for developing countries.
The research methodology used in this study involves collecting and analyzing data using bibliometric analysis tools. Bibliometric analysis is a quantitative method that examines the patterns and relationships within the literature of a particular field. It is based on the use of statistical techniques to analyze and map the citation patterns and co-occurrence of terms in a collection of scientific articles.
The data for this study was collected from the Web of Science (WoS) platform. WoS is a comprehensive database of scholarly literature in various fields, including economics, business, and environmental science. The study focused on publications from 1987 to 2022 that addressed the relationship between foreign direct investment flows and environmental regulation.
The inclusion criteria for selecting articles from the WoS platform included articles, books, conference papers, editorials, notes, and reviews related to the research topic. This ensured that the study included a broad range of literature on the subject. The selected articles were then analyzed using bibliometric analysis tools such as bibliographic coupling, co-citation analysis, and co-word analysis.
Bibliographic coupling analysis is a method of identifying the relationships between articles based on their shared references. Co-citation analysis is a technique that examines the frequency with which two articles are cited together in other articles. Co-word analysis, on the other hand, involves analyzing the frequency with which specific words or phrases occur together in the titles or abstracts of articles.
By using these bibliometric analysis tools, the study was able to identify the most cited articles, authors, and journals related to the research topic. This provided a comprehensive overview of the state of research on the topic and helped to identify potential research gaps and areas for further investigation. Five sets of keywords were used as a search engine for the bibliometric analysis, as we can see in Table 2.
Table 2:
Keywords used and number of papers collected for bibliometric analysis
Keywords |
Number of works |
Environmental regulation 'and ISD |
185 |
Pollution haven Theory |
54 |
True Cost Theory |
13 |
Convergence Theory |
26 |
Race to the top Theory |
179 |
Source: authored by
For the analysis of the collected databases, we used bibliometrix software, specially designed for bibliometric studies. Using this tool, we efficiently and systematically analysed the literature, identifying trends, connections and central themes of the literature analysed.
In summary, the research methodology used in this study involved collecting data from the WoS platform and analyzing it using bibliometric analysis tools such as bibliographic coupling, co-citation analysis, and co-word analysis. This methodology allowed for a comprehensive analysis of the literature on the relationship between foreign direct investment flows and environmental regulation.
Next, we will conduct bibliometric analysis for the databases obtained from the information collection process. It is important to note that the number of articles in the literature related to true cost and convergence theory is small, and the results of the analysis were found to be irrelevant. This suggests that these theories are not major topics of interest in the current literature and therefore cannot adequately explain the relationship between environmental regulation and ISD. This highlights the need to explore alternative theories and approaches to better understand this complex and dynamic relationship.
Environmental regulations and ISD
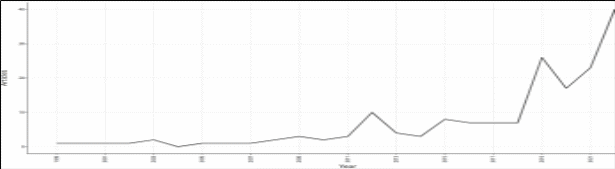
After collecting and filtering the results, a total of 185 papers were obtained and processed in bibliometrix. First of all, we aimed to test the topicality of this theme, which is why we followed the evolution of the annual production of articles on this topic. The results can be seen in Figure 1
Figure 1:
Annual scientific output - Media regulations and ISD

Source: author's own processing in bibliometrix
Based on Figure 1, it is evident that there has been a rise in the number of academic articles dedicated to investigating the connection between environmental regulation and inflow of foreign direct investment. This observation points towards the growing interest of scholars in this area. We believe that this trend will continue to grow in the future due to the consequences and importance of ISD flows in the sustainable development of national economies.
Figure 2:
Cluster network analysis - Environmental regulations and ISD

Source: developed by the author in bibliometrix
The analysis of the research clusters (Figure 2) found that there are two main clusters, namely one dealing with ISD and economic growth and another involving a number of related topics such as energy consumption, pollution, innovation, performance, environment, competitiveness, carbon emissions and financial development. These topics are at the heart of the articles reviewed, indicating their importance in environmental regulation and ISD research.
At the same time it is highlighted that the pollution haven theory is a significant topic that is part of this network. This observation implies that several authors view the relationship between environmental regulation and ISD flows through the lens of the convergence theory. Additionally, we observe that environmental regulations and ISD flows are linked to environmental issues and economic development, emphasizing their significance. As a result, we propose that scholars should focus on these themes, particularly those in cluster 2 (blue), to gain a more comprehensive understanding and enhance the connection between environmental regulations and ISD inflows. To improve and expand our understanding of the relationship between environmental regulation and ISD, researchers could also explore other variables and mechanisms that influence this relationship, such as institutional, political and cultural factors. This would allow the identification of more effective strategies tailored to different national and international contexts to balance the need for economic growth with responsibility for environmental protection and sustainable development.
Pollution paradise theory
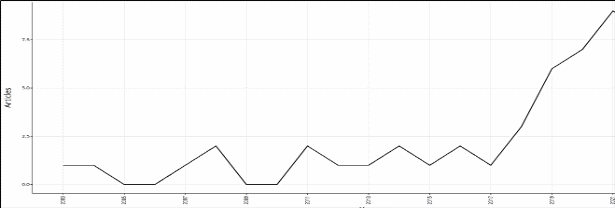
Applying the same research strategies as in the previous case, we analyzed the scientific publications that have as a theme the theory of pollution paradise (see Figure 3). Thus, in order to analyse whether this theory is of interest we analysed the scientific production on this topic, as can be seen in Figure 3.
Figure 3:
Annual scientific output - Pollution paradise theory
Source: developed by the author in bibliometrix
Here again, we can see an increase in the number of scientific publications that focus on the pollution haven theory. This indicates that the topic is of interest to researchers, moreover, it is in an increasing trend, i.e. more and more researchers are interested in this theory. Following the cluster analysis on this theme we obtained Figure 4.
Figure 4:
Cluster Network Analysis - Pollution Haven Theory

Source: developed by the author in bibliometrix
In this case, the bibliometric analysis of network co-occurrence reveals a diversification of discussions on pollution haven theory, as we identified a larger number of clusters (7 clusters). The results indicate that pollution haven theory is closely related to topics such as the environment, emissions, air pollution, international trade, economic growth and environmental and societal impacts. It is also interesting to note the presence of China in this network, suggesting that this country exerts a significant impact on environmental and ISD issues, which could be the subject of further specific research.
The areas of focus related to pollution haven theory and ISD are policy, environmental regulation, and economic and environmental performance. Researchers are urged to pay important attention to these areas when considering this theory, as they can help develop a comprehensive understanding of the relationship between environmental regulation and ISD. The analysis reveals a strong link between the pollution haven theory and economic growth, indicating that environmental problems are closely related to economic development. There is a need to examine and assess the influence of environmental regulations on economic expansion and to find solutions to facilitate sustainable development and environmental conservation at the same time.
In summary, the co-occurrence network analysis conducted through bibliometrics underscores the significance of themes connected to emissions, pollution, global trade, and economic growth when examining the discourse on pollution haven theory and ISD. The results suggest that researchers and policy makers should consider these topics in the development of coherent and integrated policies and strategies to promote foreign direct investment in a manner consistent with environmental protection and sustainable development goals.
c) Race up theory
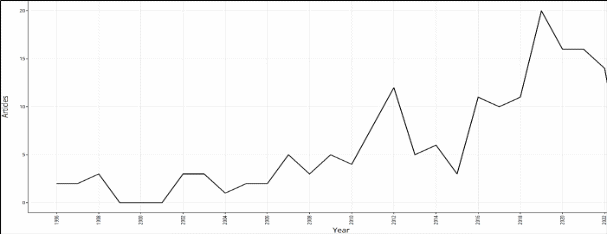
In the following, we will analyse whether the race-up theory is of research interest, which is why we have analysed the scientific output on this topic, as shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5:
Annual scientific output - Race theory up
Source: developed by the author in bibliometrix
Unlike the pollution paradise theory, we see that interest in the race to the top theory is not on an upward trend. Since 2019, the interest of researchers in this theory has decreased, as we can see in the figure above. Which is why we refute hypothesis #2 of this paper, namely: the race up theory is the one that has the most support in the literature. Consequently, we can state that the theory that enjoys the greatest popularity at present is the pollution paradise theory. Following the cluster analysis on this theme we obtained Figure 6.
Figure 6:
Cluster Network Analysis - Race Up Theory

Source: developed by the author in bibliometrix
The cluster network analysis (see Figure 6) highlights 5 research clusters in terms of the race up theory, with a variety of topics being addressed in the literature on this topic. These clusters highlight the importance of different aspects related to race-up theory and how they influence the attractiveness of ISD.
In the first cluster, we see terms such as race, gender, women and diversity. This reveals to us that these topics are closely related to race theory upwards and can be considered important factors in determining the attractiveness of ISD. This finding suggests that researchers and policy makers should address issues of diversity and inclusion when analysing and developing strategies to attract ISD. In the second cluster, it highlights the role of public policies, such as race-criticism theory and affirmative action, in encouraging competition among states to attract ISD and improve economic performance. This highlights the importance of developing equitable and inclusive public policies to create an attractive environment for investors. In the third important cluster, issues of governance and competition between states to attract ISD are discussed. This suggests that attracting ISD requires effective and transparent governance, as well as the promotion of a stable and supportive business environment. The last two clusters of research focus on scientific models and legal aspects, emphasizing the significance of a sound legal framework and innovation in attracting ISD. This suggests that countries should invest in R&D and maintain a sound legal framework to promote an attractive business environment for investors.
Taken together, these results illustrate the complex connections between race to the top theory and ISD and highlight the importance of factors such as diversity, public policy, governance and education in creating an environment conducive to ISD and economic performance. The results suggest that researchers and policy makers should consider these issues in formulating and implementing strategies to attract ISD and promote sustainable and inclusive development.
The bibliometric analysis showed that interest in the relationship between environmental regulation and ISD is growing, with two main clusters identified in the literature. The importance of topics such as energy consumption, pollution, innovation, performance, environment, competitiveness, carbon emissions and financial development was highlighted in the analysis. Hypothesis H1, which states that favourable tax regulations, green technology and quality of education are key factors in attracting foreign direct investment, was confirmed by the results. The findings of the analysis indicate an increasing interest in the pollution haven theory and its connection to topics such as emissions, air pollution, international trade, and economic growth. Thus, the hypothesis that the race to the top theory has the most support in the literature (H2) is refuted.
The relationship between environmental regulation and ISD attraction is multifaceted and intricate, involving various theories and approaches. By utilizing bibliometric methods and reviewing the literature, we obtained a clearer understanding of the ongoing debate and the state of research in this area. Furthermore, the research highlights the necessity of developing coherent and comprehensive policies that foster foreign direct investment while upholding environmental protection objectives. Effective and transparent governance, as well as a conducive and stable business environment, are crucial in attracting ISD. Additionally, the significance of legal frameworks and innovation in attracting ISD is highlighted in the last two clusters, which focus on scientific models and law.This would mean close collaboration between governments, business and international organisations, and is the only option to create a framework for sustainable development and innovation in green technologies. At the same time, there is a strong need for further research in this area to identify the most effective approaches and strategies to attract ISD without compromising environmental protection and sustainable development. This will allow for more informed policy recommendations tailored to the specific context of each country, thus contributing to the achievement of the global goals of combating climate change and environmental degradation.
The limitations of the research are: First off, the study did not take into account how various geographic contexts and locations can affect how environmental regulation and foreign direct investment are related. This could be a drawback because regional variations might alter how these variables are related. The study's focus was on the more general relationship between environmental regulation and foreign direct investment, which was the justification for this choice.
Second, the study did not examine how other facets of the relationship between environmental regulation and foreign direct investment, such as cultural and social features, might play a role. This is a drawback since these variables could harm foreign direct investment by interacting with environmental laws.
The study's investigation of the literature on the connection between environmental regulation and foreign direct investment solely relies on bibliometric approaches. This methodology is helpful in spotting patterns and trends in the literature, but it does not fully explain the underlying causes that might affect how these variables interact. Hence, in order to provide a more thorough grasp of the subject, future research may need to combine different techniques.
REFERENCES
Agyapong, D., & Bedjabeng, K. A. (2020). External debt stock, foreign direct investment and financial development: Evidence from African economies. Journal of Asian Business and Economic Studies, 27(1), 81-98.
Ahmad, M., Jiang, P., Majeed, A., & Raza, M. Y. (2020). Does financial development and foreign direct investment improve environmental quality? Evidence from belt and road countries. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27, 23586-23601.
Alsaifi, K., Elnahass, M., & Salama, A. (2020). Carbon disclosure and financial performance: UK environmental policy. Business Strategy and the Environment, 29(2), 711-726.
Balsalobre-Lorente, D., Driha, O. M., Shahbaz, M., & Sinha, A. (2020). The effects of tourism and globalization over environmental degradation in developed countries. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27, 7130-7144.
Becker, W., Domínguez-Torreiro, M., Neves, A. R., Moura, C. T., & Saisana, M. (2021). Exploring the link between Asia and Europe connectivity and sustainable development. Research in Globalization, 3, 100045.
Caetano, R. V., Marques, A. C., Afonso, T. L., & Vieira, I. (2022). A sectoral analysis of the role of Foreign Direct Investment in pollution and energy transition in OECD countries. Journal of Environmental Management, 302, 114018.
Chau, K. Y., Lin, C. H., Tufail, B., Tran, T. K., Van, L., & Nguyen, T. T. H. (2022) Impact of eco-innovation and sustainable tourism growth on the environmental degradation: the case of China. Economic Research-Ekonomska Istraživanja, 1-24.
Chen, M. J., & Miller, D. (2010). West meets east: Toward an ambicultural approach to management. Academy of Management Perspectives, 24(4), 17-24.
Contractor, F. J., Dangol, R., Nuruzzaman, N., & Raghunath, S. (2020) How do country regulations and business environment impact foreign direct investment (ISD) inflows. International Business Review, 29(2), 101640.
Dinh, T. T. H., Vo, D. H., The Vo, A., & Nguyen, T. C. (2019). Foreign direct investment and economic growth in the short run and long run: Empirical evidence from developing countries Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 12(4), 176.
Du, K., Cheng, Y., & Yao, X. (2021). Environmental regulation, green technology innovation, and industrial structure upgrading: The road to the green transformation of Chinese cities. Energy Economics, 98, 105247.
Duzbaievna Sharapiyeva, M., Antoni, A., & Yessenzhigitova, R. (2019). The impact of port transport-logistics infrastructure and LPI for economic growth: on the example of landlocked countries. Pomorstvo, 33(1), 63-75.
Gereffi, G., Humphrey, J., & Sturgeon, T. (2005). The governance of global value chains. Review of International Political Economy, 12(1), 78-104.
Giuliani, E., & Meliciani, V. (2021). The impact of cultural and linguistic distances on the relationship between environmental regulation and foreign direct investment in the international location of US firms. Journal of World Business, 56(1), 101086.
Hossain, M. S., Kamal, M. S., Halim, M. R., & Zayed, N. M. (2019). Inward Foreign Direct Investment and Welfare Nexus: the Impact of Foreign Direct Investment on Welfare in Developing Countries. International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues, 9(4), 228.
Huynh, C. M. (2021). Foreign direct investment and income inequality: Does institutional quality matter?. The Journal of International Trade & Economic Development, 30(8), 1231-1243.
Jushi, E., Hysa, E., Cela, A., Panait, M., & Voica, M. C. (2021). Financing growth through remittances and foreign direct investment: Evidence from Balkan Countries Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 14(3), 117.
Khan, A., Chenggang, Y., Hussain, J., & Kui, Z. (2021). Impact of technological innovation, financial development and foreign direct investment on renewable energy, non-renewable energy and the environment in belt & Road Initiative countries. Renewable Energy, 171, 479-491.
Li, K., Zu, J., Musah, M., Mensah, I. A., Kong, Y., Owusu-Akomeah, M., ... & Agyemang, J. K. (2022). The link between urbanization, energy consumption, foreign direct investments and CO2 emanations: An empirical evidence from the emerging seven (E7) countries. Energy Exploration & Exploitation, 40(2), 477-500.
Majeed, A., Jiang, P., Mahmood, A., Khan, M. A., & Olah, J. (2021). The impact of foreign direct investment on financial development: new evidence from panel cointegration and causality analysis. Journal of Competitiveness, 13(1), 95.
Nasir, M. A., Huynh, T. L. D., & Tram, H. T. X. (2019) Role of financial development, economic growth & foreign direct investment in driving climate change: A case of emerging ASEAN Journal of environmental management, 242, 131-141.
Nguyen, M. L. T. (2022) Foreign direct investment and economic growth: The role of financial development. Cogent Business & Management, 9(1), 2127193.
Osei, M. J., & Kim, J. (2020). Foreign direct investment and economic growth: Is more financial development better?. Economic Modelling, 93, 154-161.
Park, S. H., & Luo, Y. (2001). Guanxi and organizational dynamics: Organizational networking in Chinese firms. Strategic Management Journal, 22(5), 455-477.
Peng, X., & Wang, Q. (2006) Environmental Regulation and Foreign Direct Investment: Evidence from China. Journal of World Business, 41(1), 34-46. doi: 10.1016/j.jwb.2005.09.007
Prus, P., & Sikora, M. (2021). The impact of transport infrastructure on the sustainable development of the region-Case study. Agriculture, 11(4), 279.
Rezza, G. (2015). Pollution haven hypothesis: A systematic review of the evidence. Journal of Economic Surveys, 29(3), 591-611.
Saidi, S., Mani, V., Mefteh, H., Shahbaz, M., & Akhtar, P. (2020). Dynamic linkages between transport, logistics, foreign direct Investment, and economic growth: Empirical evidence from developing countries. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 141, 277-293.
Saidi, S., Mani, V., Mefteh, H., Shahbaz, M., & Akhtar, P. (2020). Dynamic linkages between transport, logistics, foreign direct Investment, and economic growth: Empirical evidence from developing countries. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 141, 277-293.
Slangen, A. H., & Van Tulder, R. (2009). Cultural distance, political risk, or governance quality? Towards a more accurate conceptualization and measurement of external uncertainty variables. International Business Review, 18(3), 276-291.
Wang, H., & Li, J. (2021). Dual effects of environmental regulation on PM2. 5 pollution: Evidence from 280 cities in China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(34), 47213-47226.
Xiao, D., Gao, L., Xu, L., Wang, Z., & Wei, W. (2023) Revisiting the Green Growth Effect of Foreign Direct Investment from the Perspective of Environmental Regulation: Evidence from China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(3), 2655.
Yang, X., & Shafiq, M. N. (2020). The impact of foreign direct investment, capital formation, inflation, money supply and trade openness on economic growth of Asian countries. iRASD Journal of Economics, 2(1), 25-34.